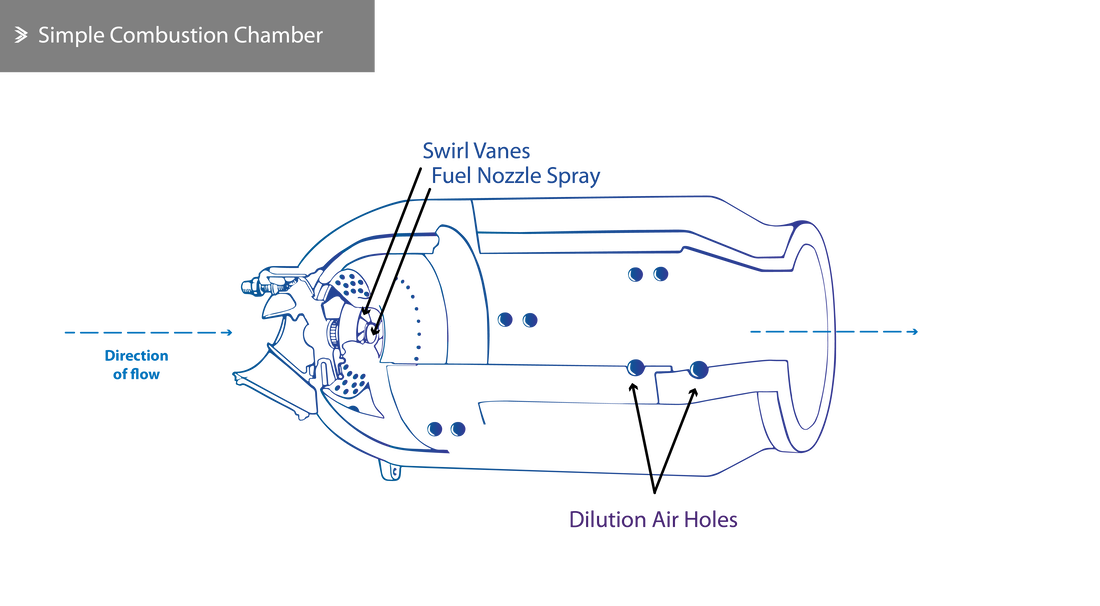
Aeolus Combustion Chambers JetX Engineering
The purpose of a jet engine is to move the airplane with some amount of thrust, in the forward direction. Change in momentum of the flowing air in between the inlet and outlet section of the jet engine results in the generation of the required thrust force. Usually a jet engine works on a fan, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine and a nozzle.
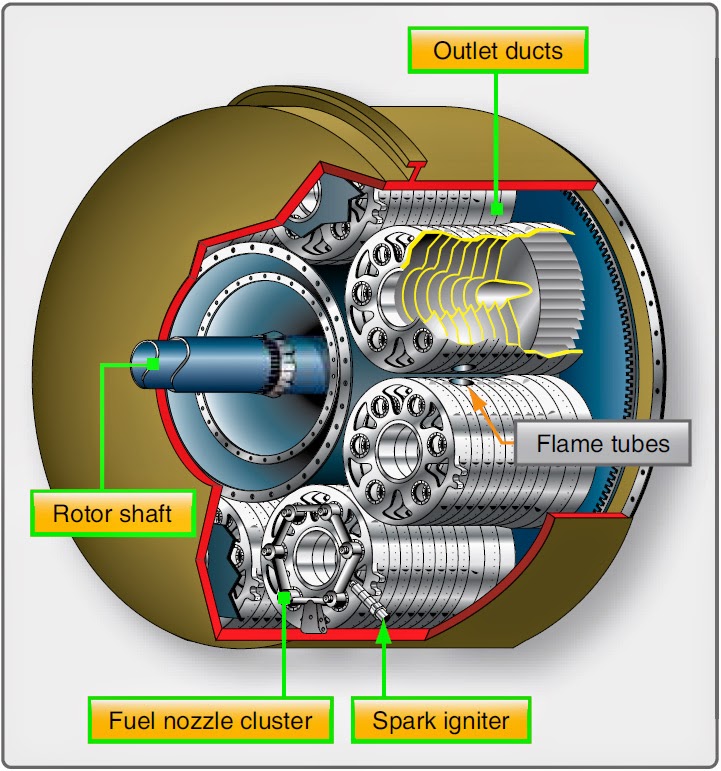
Aircraft systems Gas Turbine Engine Combustion Section
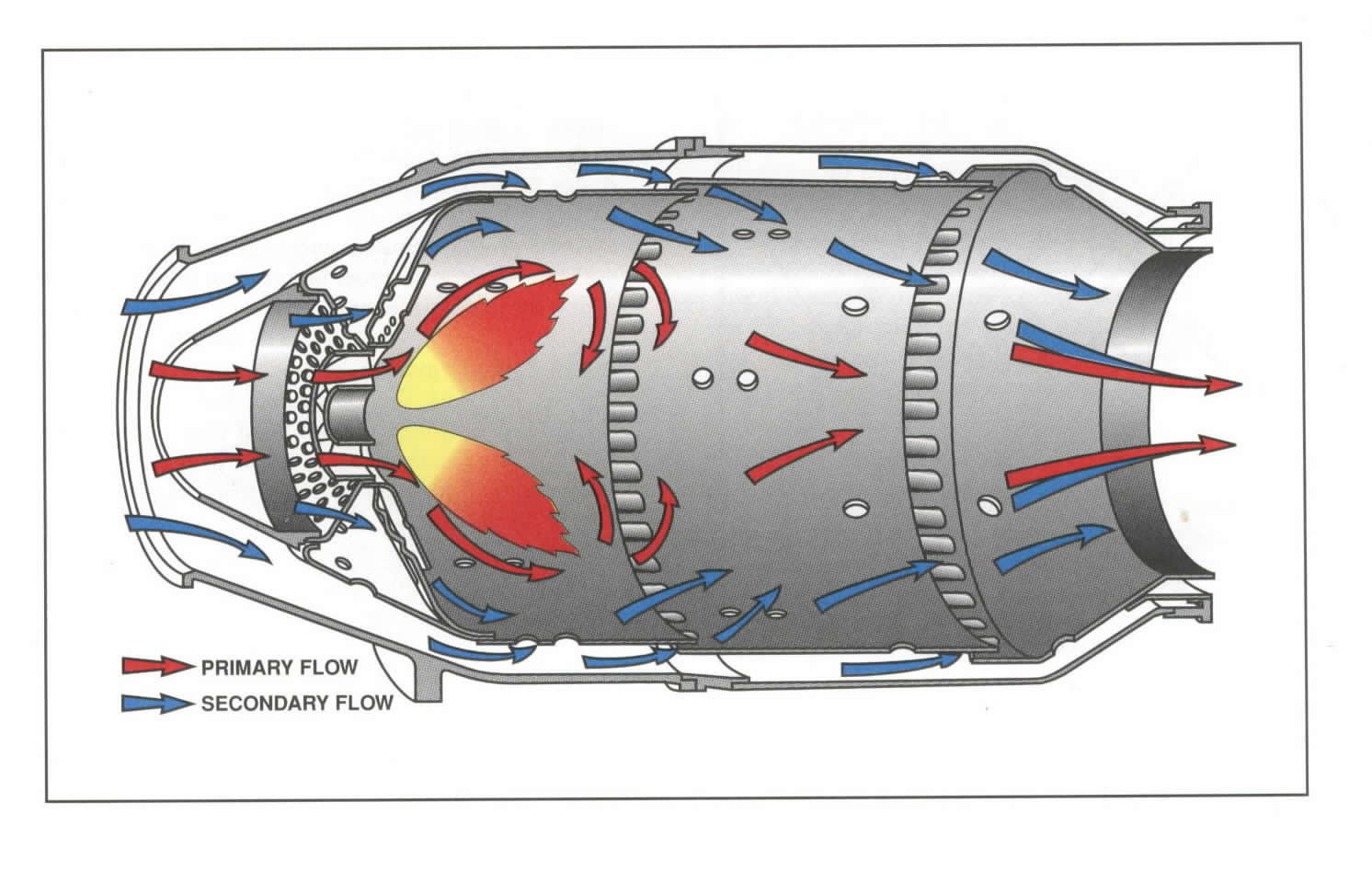
The combustion chamber in gas turbines and jet engines (including ramjets and scramjets) is called the combustor . The combustor is fed with high pressure air by the compression system, adds fuel and burns the mix and feeds the hot, high pressure exhaust into the turbine components of the engine or out the exhaust nozzle.

Jet Engine with Multiple Combustion Chambers Stock Photo Image of
Jet engines move the airplane forward with a great force that is produced by a tremendous thrust and causes the plane to fly very fast.. The squashed air is forced into the combustion chamber. Combustor - In the combustor the air is mixed with fuel and then ignited. There are as many as 20 nozzles to spray fuel into the airstream.

How Does A Turbofan Engine Work? Gas turbine, Jet engine, Turbine engine
jet engine, any of a class of internal-combustion engines that propel aircraft by means of the rearward discharge of a jet of fluid, usually hot exhaust gases generated by burning fuel with air drawn in from the atmosphere.. General characteristics. The prime mover of virtually all jet engines is a gas turbine.Variously called the core, gas producer, gasifier, or gas generator, the gas turbine.
Combustion chamber, jet engine / flame tube, jet engine / sectio
A gas turbine jet engine works by compressing air, mixing it with fuel, igniting the mixture, and ejecting the air behind the engine, creating a pushing force known as thrust.. The compressed air then moves into the combustion chamber, setting the stage for the next step. Step 3: Combustion. Here comes the combustion. Fuel injectors spray a.

Jet engine video 1 overview of the combustion chamber. YouTube
This paper deals with the modelling and flow simulation in the combustion chamber of a turbojet engine in order to find the optimal velocity, pressure and temperature distributions in the flame.

What is a Gas Turbine Engine? (with pictures)
Types of jet engines. All jet engines and gas turbines work in broadly the same way (pulling air through an inlet, compressing it, combusting it with fuel, and allowing the exhaust to expand through a turbine), so they all share five key components: an inlet, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine (arranged in exactly that sequence) with a driveshaft running through them.

Jet engine with noninline combustion chambers BonzoESC Flickr
A jet engine is an aircraft engine used to provide p ropulsion for a vehicle by ejecting a substance flow, i.e., creating a reactive force (thrust) which is applied against the vehicle.. The air is heated by the fuel combustion in the combustion chamber to a temperature T g and then is expanded first in the turbine.
JET FUEL TURBINE ENGINES
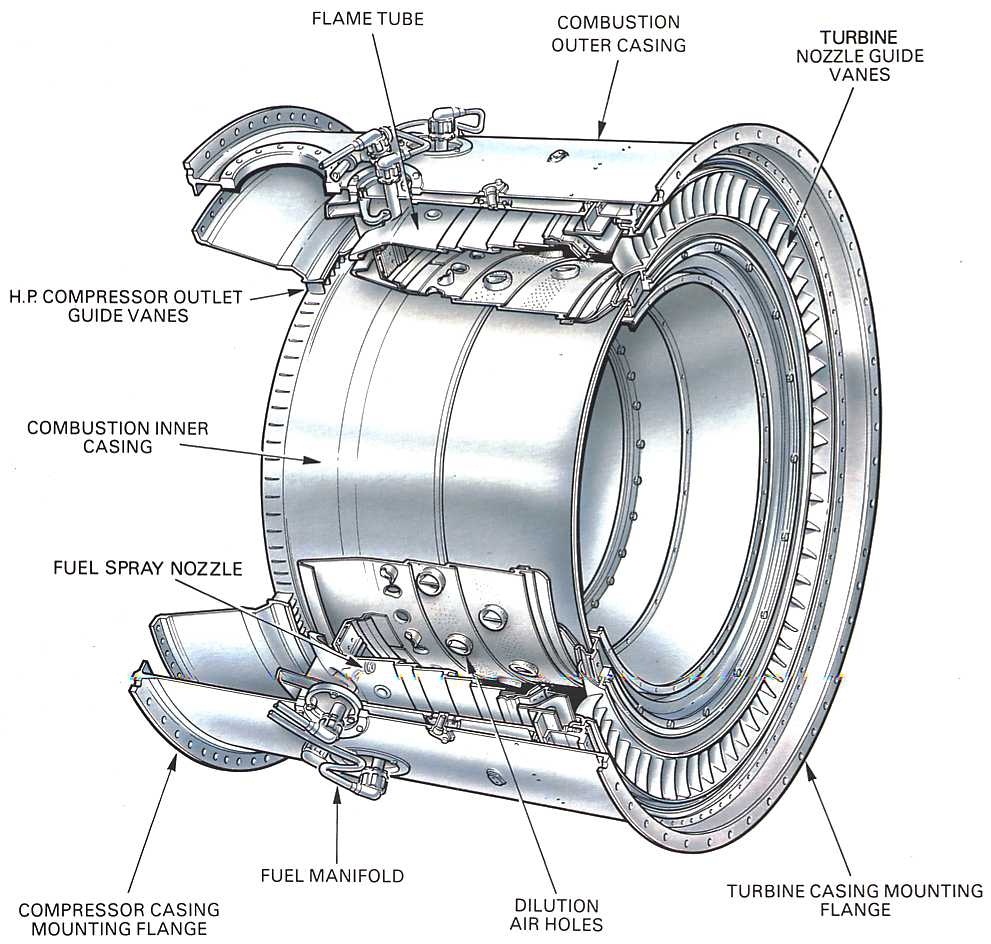
Failures in operating engines are seldom attributable to the combustor, except perhaps when maintenance is given a short shrift. The combustion chambers and the region around the turbine entry are, therefore, the subject of scrutiny by the people who maintain jet engines. Figure 12.5 also illustrates the need to keep the combustion chamber.

SRN4 Features Tour jameshovercraft.co.uk
Description. Combustion Chambers for Jet Propulsion Engines focuses on the design of combustion chambers for turbo-jet and ramjet engines, including reheat systems. This compilation, which is a training manual for the combustion chamber course held in the Moscow Aeronautical Institute, provides a general presentation of the basic elements of.
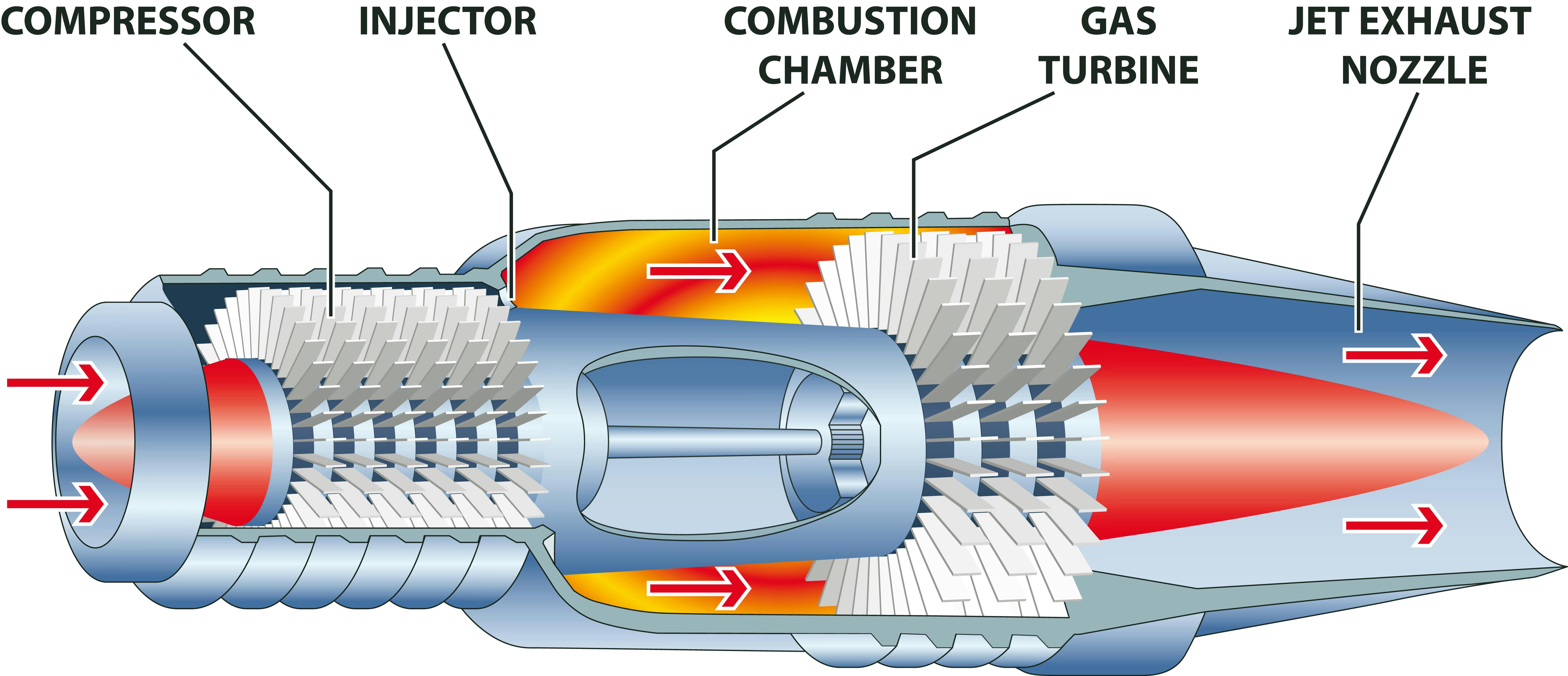
Jet Engine Major Components How Do They Work? Xometry
In this paper are presented some results about the study of combustion chamber geometrical configurations that are found in aircraft gas turbine engines. The main focus of this paper consists in a study of a new configuration of the aircraft engine combustion chamber with an optimal distribution of gas velocity in front of the turbine.
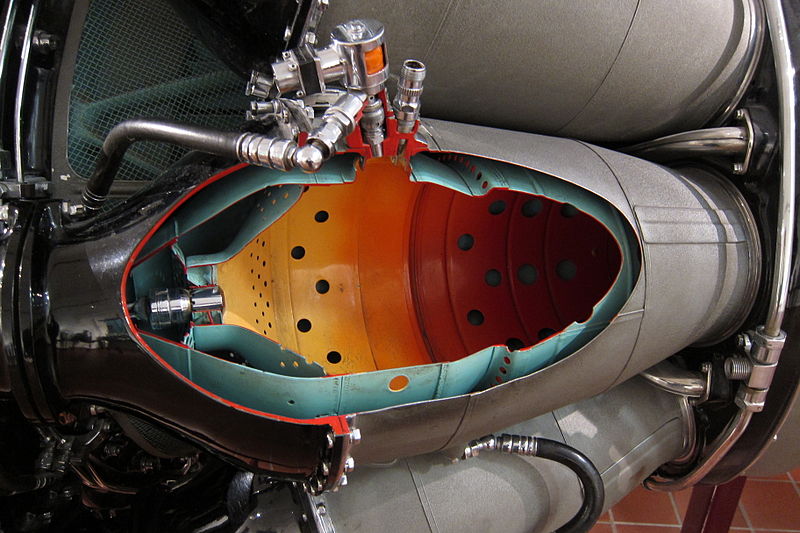
Meteorología aeronáutica y conocimientos generales de aviación CÁMARAS
COMBUSTION CHAMBER- The part of a jet engine where high pressure air from the compressor is mixed with fuel and is then burned. COMPRESSOR- The compressor is the center of the jet engine. It is composed of a series of spinning blades that suck air through an inlet and compress the air. It is then passed on to the combustion chamber in which it.

model aircraft INTRODUCTION An early combustion chamber.
A combustor is a component or area of a gas turbine, ramjet, or scramjet engine where combustion takes place. It is also known as a burner, burner can, combustion chamber or flame holder.In a gas turbine engine, the combustor or combustion chamber is fed high-pressure air by the compression system. The combustor then heats this air at constant pressure as the fuel/air mix burns.
singlestageturbojet
Combustion Chambers. 4.4 Combustion Chamber Efficiency. As the name suggests, the combustion chamber is designed to combust large quantities of fuel, mixed with even larger quantities of air which leaves the compressor. The combustion must be done in such a way that allows the air to expand and accelerate without causing instabilities over the.
model aircraft COMBUSTION CHAMBER PERFORMANCE
The image above shows how a jet engine would be situated in a modern military aircraft. In the basic jet engine, air enters the front intake and is compressed (we will see how later). Then the air is forced into combustion chambers where fuel is sprayed into it, and the mixture of air and fuel is ignited. Gases that form expand rapidly and are.
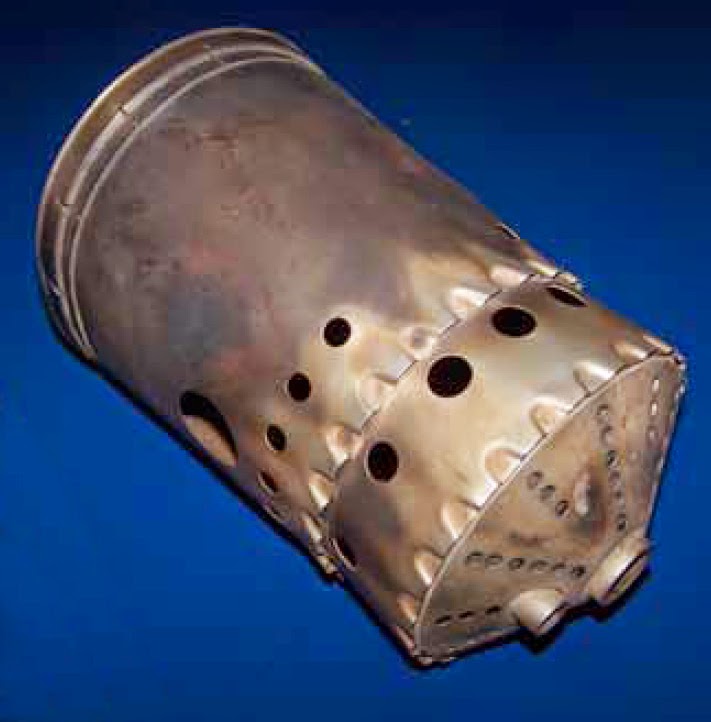

Aircraft systems Gas Turbine Engine Combustion Section
Active pre-chamber turbulent jet ignition with a high compression ratio has been demonstrated to be an effective method for significantly enhancing engine thermal efficiency. A dual modification of the combustion chamber and the pre-chamber was performed on an AVL 5400 single-cylinder Miller engine to achieve stable ultra-lean burn at a high compression ratio, and a breakthrough of 51.10%.